| Transforming Cardiovascular Care and Improving Heart Health | SIGN UP ⋅ SHARE |
|
|
 
|
First Focus
|
Pediatric hospitalists play a crucial role in stewardship to combat antimicrobial resistance, with 30% to 50% of antibiotics in hospitals potentially inappropriately prescribed, according to experts. Pediatric-specific data and strategies are needed for effective stewardship, such as using pediatric-specific antibiograms and engaging stakeholders like pharmacists and infection prevention teams.
|
|
|
Drug interactions with ibrutinib do not significantly affect survival in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia but are linked to a higher risk of infection-related hospitalizations, according to a study in the British Journal of Haematology. The study highlights a pressing need for monitoring, dose adjustments and proactive infection prevention, especially when using CYP3A inhibitors.
|
|
| |
 |
| (FluxFactory/Getty Images) |
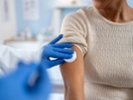
Research presented at the European Society of Cardiology Congress highlights the cardiovascular benefits of vaccines against influenza, respiratory syncytial virus and herpes zoster. The studies showed that these vaccines can reduce hospitalizations and cardiovascular events, even though messaging focused on cardiovascular benefits did not increase vaccine uptake.
|
|
A hypothetical trial simulation using data from 15 ICUs found vancomycin use in ICU patients was associated with a higher risk of acute kidney injury by day 14 of treatment, compared with alternatives such as clindamycin and linezolid. The study, published in the journal Pharmacoepidemiology Drug Safety, noted that while there was no difference in AKI risk within the first two days of treatment, the risk increased over two weeks. |
|
|
|
|
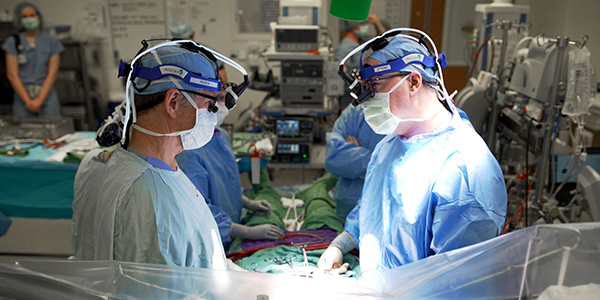
Dr. Michael Reardon and Dr. Marvin Atkins discuss the legendary origins and extraordinary legacy of Houston Methodist's Heart Tumor Program, the world's leading medical destination for complex cardiac sarcoma treatment.
|
|
|
|
|
|
 
|
Practice & Hospital Management
|
Hospital leaders are encouraged to actively engage with AI to better understand its impact and serve as role models for their staff. By integrating AI into workflows, executives can gain firsthand experience and effectively evaluate AI's real-world applications. "You cannot take full advantage of [AI] if you don't have that level of operational discipline and knowledge to know how this tool, this capability, this new thing can completely transform and change the way that we think about that process," Fairview Health Services President and CEO James Hereford said.
|
|
|
 | What Gut Health Means for Your Practice
There is mounting evidence the gut microbiota plays an important role in human health and disease, including cardiovascular disease. Find research and a nutritional analysis guide to help you discuss the benefits of avocados for the gut microbiome with your patients. Download the fact sheet. |
|---|
| |
|
|
 
|
Innovation & Technology Trends
|
Multimodality imaging is becoming essential in cardiac care, requiring specialists trained in nuclear medicine, echocardiography, cardiac MRI and CT, according to Dr. Wael Jaber, director of nuclear cardiology and professor of medicine at Cleveland Clinic. "Patients don't ask to see a nuclear cardiologist or a heart failure doctor," Jaber said. "They come with a problem, and it's the team that solves it. The team is here to stay -- and I can't see us going back to fragmentation."
|
|
|
Hospitals in socioeconomically disadvantaged areas are significantly behind in adopting health information technology such as telehealth and joining a health information exchange, according to a study in JAMA Health Forum. The study cites barriers like limited infrastructure and funding, though it notes that adoption has increased overall since 2018.
|
|
|
 | Building a Scalable Customer 360 in Healthcare
On October 2 at 1 PM EST, discover how to link data across platforms and tackle governance challenges. Learn from Baylor Scott & White's digital and analytics leaders in this webinar to find out how they replaced IBM initiate and built a phased Customer 360 to unify 46M identities across Epic, Snowflake, and JV Systems.
Register Now! |
|---|
| |
|
|
 
|
Play Paths to Power bonus path
|
Yeahhh… gonna need you to finish.
You've come this far. The bonus path is basically the TPS report of quests—but this one's actually fun. New chaos. Quirky riddles. And maybe even some flair. You found the Wizard of Lite, now he joins you for one final quest to truly bring calm to this digital, mystical land. Play Game
|
|
 
|
Health Equity & Prevention
|
The city of Springfield, Massachusetts, has hired a racial and health equity coordinator under the Department of Health and Human Services. Shenell Ford will collaborate with community groups to promote cultural sensitivity, expand mental health training programs and support other advancements in community health.
|
|
| |
 |
| (Pixabay) |
More than half of heart attacks in women younger than 65 stem from nontraditional causes, such as spontaneous coronary artery dissection and embolism, rather than clogged arteries, according to a Mayo Clinic study in JACC. "When the root cause of a heart attack is misunderstood, it can lead to treatments that are less effective -- or even harmful," said Dr. Claire Raphael, an interventional cardiologist at Mayo Clinic.
|
|
| | | |
